Ayushi Agrawal

Objectives of the Public Consultation Document on e-Invoicing in UAE
To help businesses adapt to digital transformation, the UAE Ministry of Finance (MoF) released a Public Consultation Document on February 7, 2025, which outlines the standard data requirements for e-invoices. The main goals of this effort are:
1. Create a common understanding of E-Invoicing rules
This means making sure everyone understands the requirements for using E-Invoicing
2. Help businesses get ready for E-Invoicing
This will assist businesses in preparing to use E-Invoicing when they are required.
3. Make sure invoice data is consistent and standardized
This will ensure that the information on invoices is the same across all types of documents, making it easier for everyone to use and understand.
What is e-Invoicing in UAE
E-invoicing is the digital version of paper or PDF invoices, using a format that can be read by machines and checked in real-time. In the UAE, a system called Decentralized Continuous Transaction Control (DCTCE) is used, where invoices are first checked by approved service providers (ASPs) before being sent to buyers and tax authorities. This helps ensure that invoices are accurate, clear, and follow tax rules.
The e-Invoicing Data Dictionary (PINT AE)
The E-Invoicing Data Dictionary (PINT AE) outlines the key data fields and their characteristics for the most common types of invoices used by businesses in the UAE. It highlights the need for standardization to make sure that different invoice types are consistent. This standardization is important for smooth integration, efficient processing, and ensuring that E-Invoicing works well across the UAE’s business system.
Excluded Transaction: A business transaction that doesn’t require E-Invoicing exchange or reporting.
It is important to note that E-Invoicing will be rolled out in a phased manner.
The E-invoicing framework encompasses all Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Government (B2G) transactions, regardless of the VAT registration status of the entities involved.
Background: UAE e-Invoicing Program
The UAE E-Invoicing program aligns with global trends in Digital Reporting Requirements (DRR) and Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC), reflecting the increasing adoption of digital tax compliance measures worldwide.
We the UAE 2031 vision, are as follows:
- VAT Compliances: – Maximize VAT compliance, tackle the shadow economy, and shrink the tax gap.
- Effectiveness: Increase transparency and improve audits with a view to encouraging a long-term culture of compliance.
- Taxpayer experience: Enhance taxpayer and user experiences, potentially offering new and innovative engagements.
- Digitalization: Reduce human intervention in certain business and tax reporting processes with a view to making the UAE and its fiscal ecosystem more digitally enabled.
- Efficiency: Optimize cost and core operations, reduce processing time and encourage a reduction in paper wastage with a view to helping meet sustainability objectives.
- Economic contribution: Contribute to the growth and competitiveness of the economy and utilize big data.
- Contribute for policy making and government interventions: By adopting E-Invoicing, UAE government will have access to the relevant data in near real-time which will help in providing deep insights to policy makers for identifying areas and sectors that need government support and assistance.
Framework for e-Invoicing in UAE
The UAE e-Invoicing requirements apply to all businesses operating in the UAE, regardless of their VAT registration status, ensuring comprehensive adoption across the business ecosystem.
The UAE has implemented a Decentralized Continuous Transaction Control and Exchange (DCTCE) model, a modern approach to electronic invoicing that leverages decentralized technologies to enhance:
Efficiency – Streamlining transaction processing and reducing administrative burdens.
Security – Strengthening data protection and fraud prevention.
Transparency – Ensuring real-time visibility and compliance with regulatory requirements.
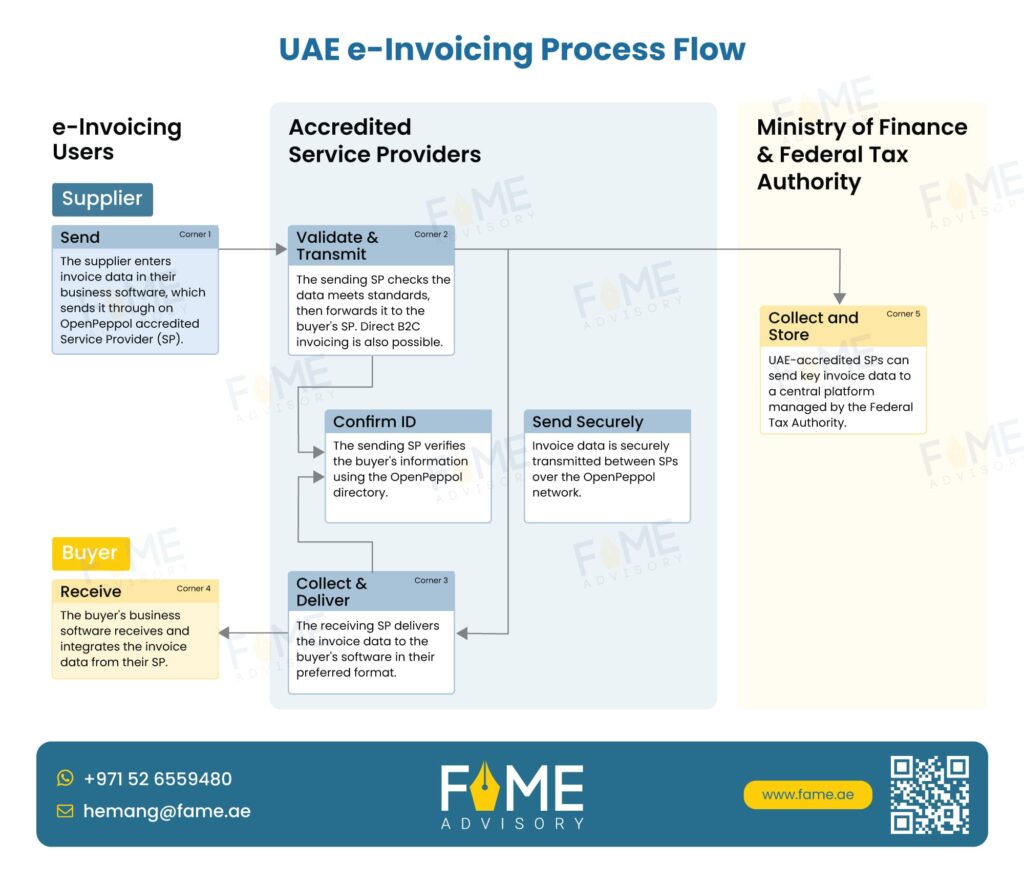
The UAE E-Invoicing process follows a structured approach involving multiple stakeholders to ensure compliance, validation, and seamless transaction processing. Below is a step-by-step breakdown of the E-Invoicing exchange and reporting mechanism:
Let’s break this process down with a simple example to explain it step by step:
Example Scenario:
- Supplier (C1) is a business that sells products.
- Buyer (C4) is the business that purchases these products.
- Corner 2 (C2) is the service provider that helps the Supplier send the eInvoice.
- Corner 3 (C3) is the service provider that helps the Buyer receive the eInvoice.
- Corner 5 (C5) is a system that handles and validates tax-related data.
UAE e-Invoicing Process: A Step-by-Step Overview
Step 1: Supplier sends the eInvoice
- Supplier (C1) creates an eInvoice in the agreed format (PINT AE format) and submits it to their service provider, Corner 2 (C2).
- Example: Supplier C1 is sending an invoice for 100 products sold to Buyer C4.
Step 2: Corner 2 validates and converts the invoice
- Corner 2 (C2) receives the eInvoice data from C1, checks if it’s correct, and if needed, converts it into the standard UAE eInvoice XML format.
- Example: C2 receives the eInvoice in the PINT AE format and converts it into the XML format used in the UAE.
Step 3: Corner 2 sends the eInvoice to the Buyer’s service provider
- C2 then sends the eInvoice (now in XML format) to Corner 3 (C3), the Buyer’s service provider and buyer will be able to see and approve.
- Example: C2 sends the invoice data to C3 so that Buyer C4 can see it.
Step 4: Corner 2 reports Tax Data to Corner 5
- Corner 2 (C2) also reports the Tax Data Document (TDD) to Corner 5 (C5), which handles tax data validation.
- Example: C2 reports the tax details related to the eInvoice to C5.
Step 5: Corner 3 validates the eInvoice
- Corner 3 (C3) checks the eInvoice received from C2 and confirms if it’s valid.
- If everything is correct, C3 sends a Message Level Status (MLS) back to C2, confirming the eInvoice has been successfully processed.
- If there’s an issue with the invoice, C3 sends a negative MLS to C2 and C5.
- Example: C3 checks the eInvoice and if it’s valid, it sends a message saying “Invoice approved” to C2.
Step 6: Corner 3 sends the eInvoice to the Buyer
- C3 sends the eInvoice to Buyer (C4) in the agreed format.
- Example: C3 delivers the approved invoice to Buyer C4.
Step 7: Corner 3 reports Tax Data to Corner 5
- If the eInvoice is validated successfully, C3 also reports the Tax Data Document (TDD) to C5.
- Example: After confirming the eInvoice is correct, C3 sends the tax details to C5 for final validation.
Step 8: Corner 5 confirms TDD reporting to Corner 2
- Corner 5 (C5) sends a confirmation MLS to C2, letting them know the TDD has been successfully reported and validated.
- Example: C5 tells C2, “The tax data has been successfully validated.”
Step 9: Corner 5 confirms TDD reporting to Corner 3
- C5 also sends a confirmation MLS to C3, letting them know that the TDD has been validated.
- Example: C5 tells C3, “The tax data has been successfully validated.”
Step 10: Corner 2 sends the MLS to Supplier
- C2 sends both the Message Level Status (MLS) from C3 (for processing the invoice) and C5 (for reporting the TDD) to the Supplier (C1).
- Example: C2 tells Supplier C1, “The invoice has been processed and tax data reported successfully.”
Step 11: Corner 3 sends the MLS to Buyer
- C3 sends the MLS received from C5 (confirming TDD reporting) to the Buyer (C4).
- Example: C3 informs Buyer C4, “The tax data for your invoice has been successfully validated.”
Summary:
In this process, the eInvoice is created by the Supplier, validated by the Service Providers (C2 and C3), and passed between them. Tax-related data is also reported to Corner 5 (C5) for validation. Once everything is confirmed, status messages (MLS) are sent back to everyone involved, ensuring that all parties are informed about the success or failure of the invoice processing.
Overview of Data Dictionary (PINT AE) in the UAE e-Invoicing Framework
Data Dictionary (PINT AE) is a fundamental component of the UAE E-Invoicing framework, providing a structured and standardized catalog of all data elements involved in generating, exchanging, processing, and reporting E-Invoicing
This includes the following:
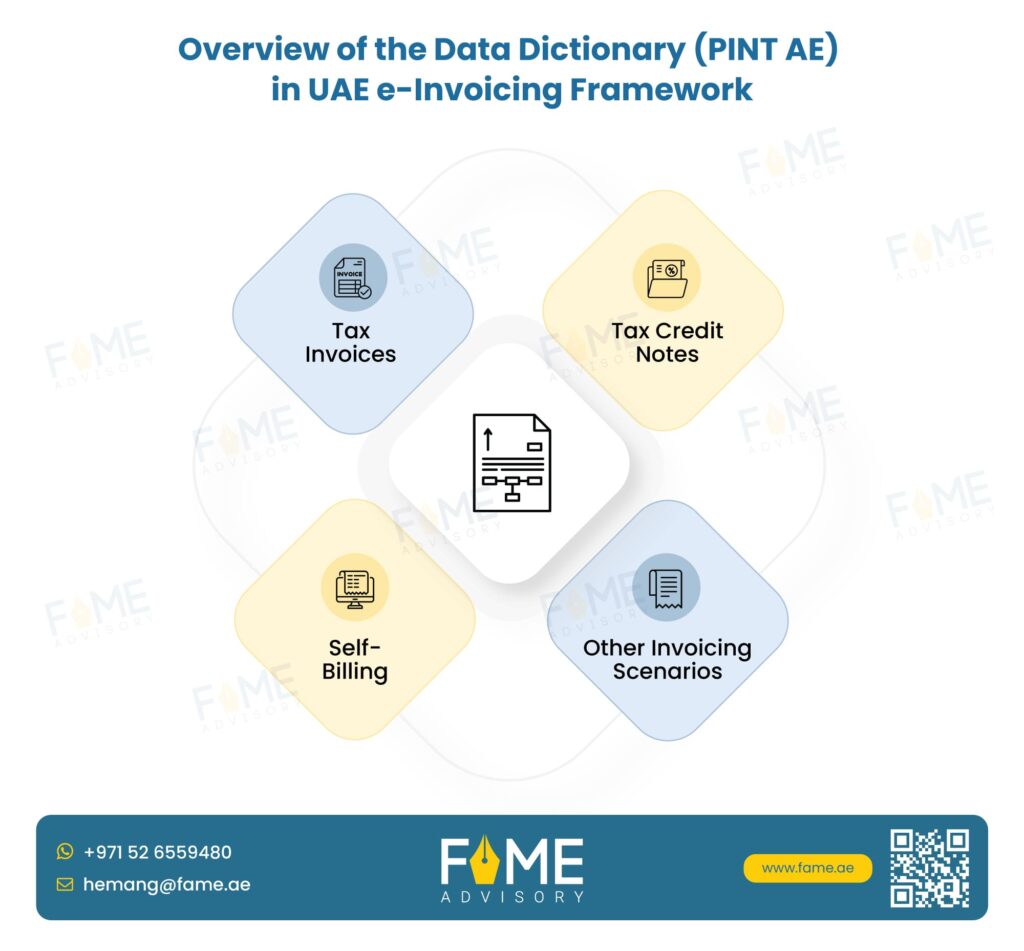
As a foundational reference, the Data Dictionary ensures the following:
- Consistency – Standardized data fields across all E-Invoicing processes.
- Interoperability – Seamless integration between businesses, software providers, and regulatory systems.
- Compliance – Alignment with UAE tax regulations and reporting requirements.
By serving as a universal guide for businesses, software developers, and regulatory bodies, the Data Dictionary plays a crucial role in ensuring a transparent, efficient, and compliant E-Invoicing system.
While we await further guidance, the Ministry of Finance (MoF) will continue to provide updates on the types of transactions and businesses that will be included in the upcoming phases of e-invoicing implementation.