Global Indian Family Enterprises: Legal, Financial and Operational Consideration
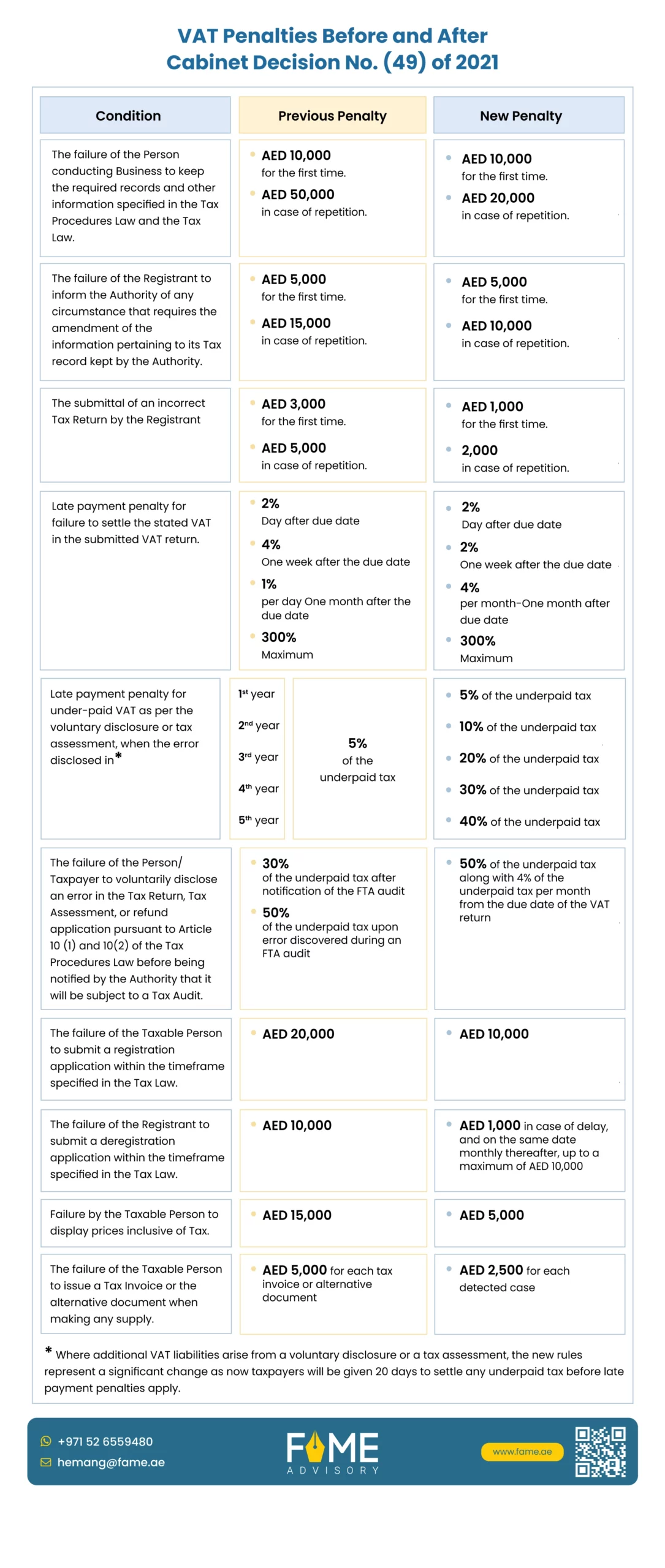
VAT Penalties and Fines in UAE: Cabinet Decision No. (49) of 2021 Impact
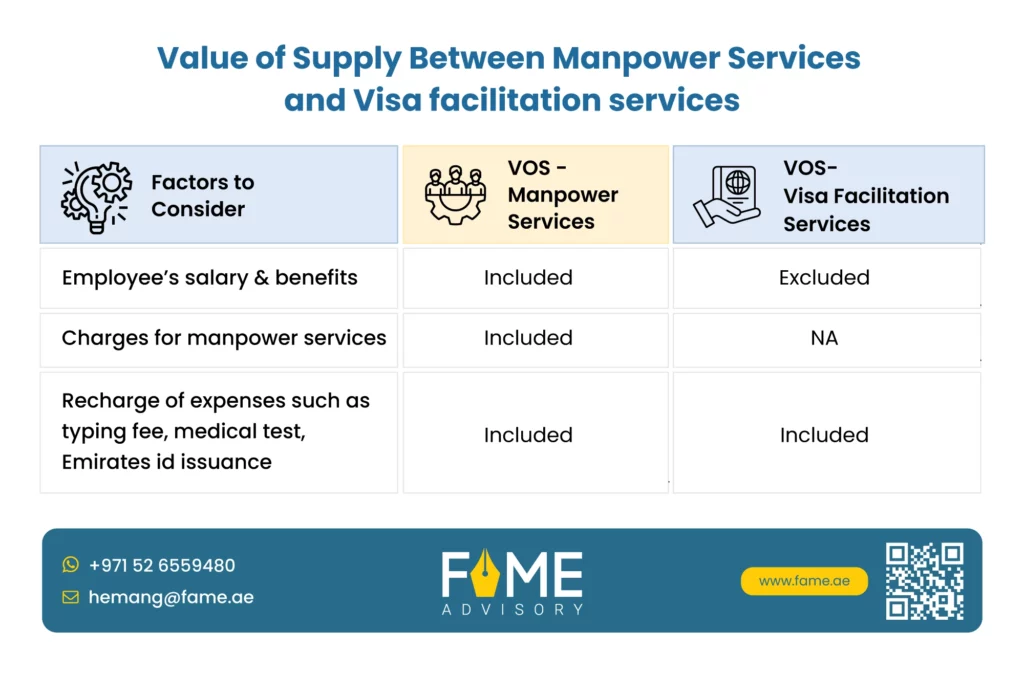
Public Clarification No. 38 (Manpower vs Visa facilitation services)
GCC Tax And Regulatory Communique May 2024
Webinar on Navigating FTA’s Free Zone Persons’ Guide
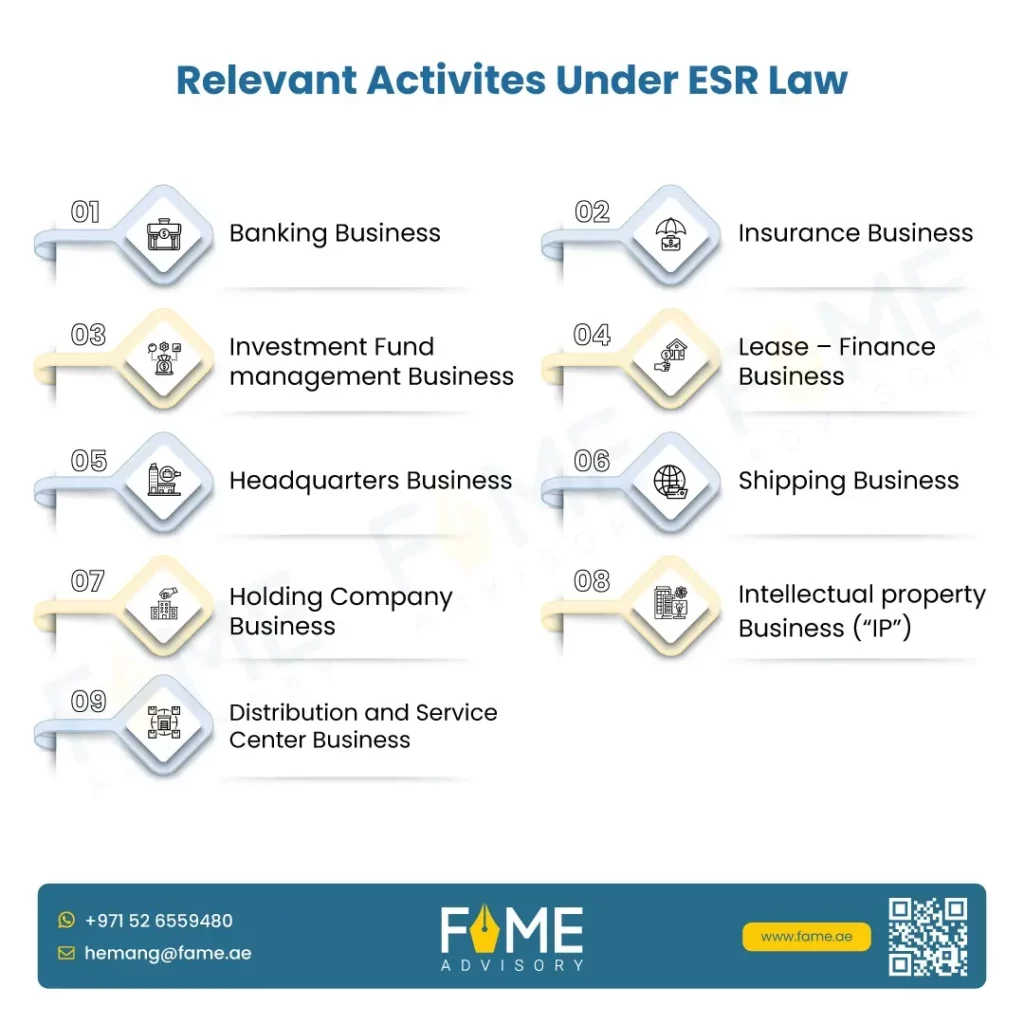
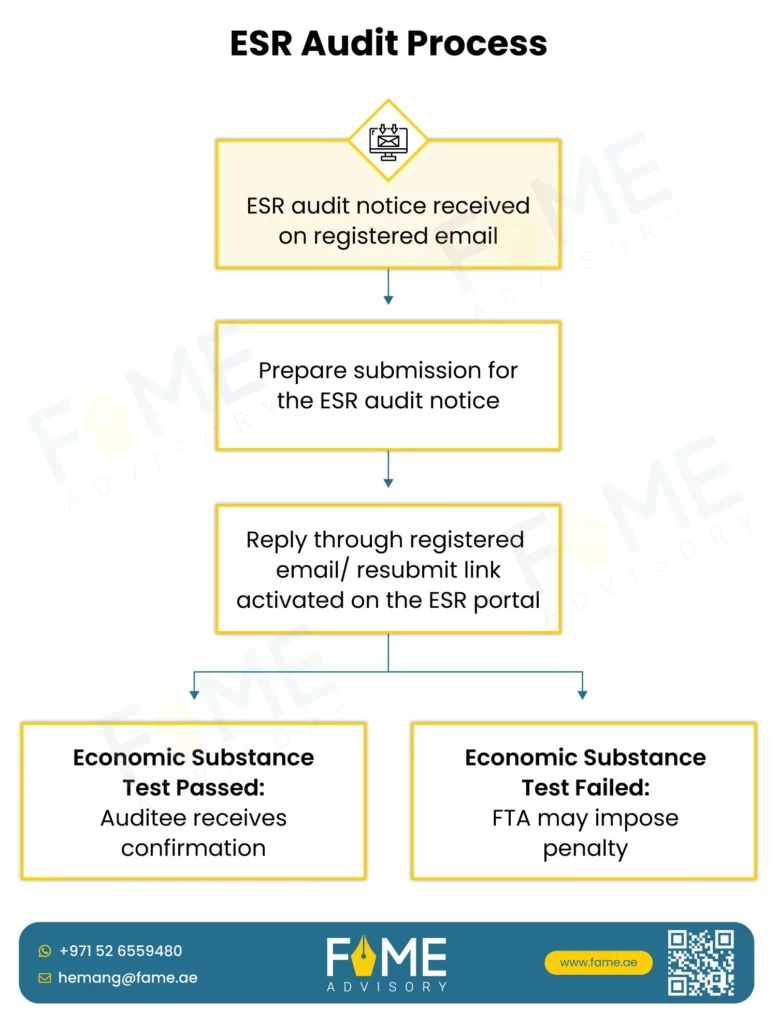
Economic Substance Regulations (ESR) Audit Intimation– Response Preparation and Documents Required
FTA Releases Guide on Free Zone Persons

The Federal Tax Authority (FTA) has finally released the much-awaited Corporate Tax (CT) guide for Free Zone entities on May 20, 2024.
This guide offers comprehensive guidance and clarity on various technical aspects for entities conducting business in a Free Zone in the UAE. It is designed to be read alongside the relevant articles of the UAE Corporate Tax Law, implementing decisions, and other guidance published by the FTA.
Below are some of the key highlights from the CT guide for Free Zone entities:
| Confirmation from Free Zone Authority: | Every Free Zone person should check with their respective Free Zone Authority to confirm if they operate in a Free Zone or Designated Zone to avail the benefit of CT@0%. There is no separate list of Free Zones/Designated zones issued for CT purposes. |
| Election: | i) A Free Zone Person will be deemed to be a Qualifying Free Zone Person (QFZP) unless they fail to meet one of the QFZP conditions or elect to be subject to tax. ii)A QFZP that elects to be subject to standard CT (i.e. 9%), or fails to meet the QFZP criteria for a specific Tax Period, will lose its QFZP status starting from the beginning of the Tax Period in which it elects to pay CT or fails to meet the criteria, as well as for the following four Tax Periods. After this period, a new election can be made if the entity wishes to continue not being treated as a QFZP unless it no longer meets the criteria of QFZP in a particular tax period. iii)The said election can be made at any point during the Tax Period in question or in the subsequent Tax Return after the Tax Period ends. This election cannot be made after the tax return filing deadline for the concerned tax period. |
| Allocation of expenses: | If a Free Zone Person generates both Qualifying Income and Taxable Income (for example, income attributable to its Foreign Permanent Establishment or Domestic Permanent Establishment), it must allocate expenses between the two and also maintain sufficient documentation that the profits attributed are commensurate with the functions performed, assets used, and risks based on the arm’s length principle. |
| Transaction between free zone persons: | In case of Qualifying Income derived from transactions between Free Zone Persons, the seller may obtain a written statement or undertaking from the purchaser affirming their role as a Beneficial Recipient and their intention to utilize the services or goods for their free zone business. |
| No income during start up phase: | A Free Zone Person who hasn’t earned any Qualifying Income in a Tax Period because they haven’t commenced revenue generation won’t lose eligibility as a QFZP, as long as they do not derive any non-qualifying revenue and fulfill all other obligations outlined in the CT Law. |
| Treatment of Tax losses: | i)Tax Losses incurred by a QFZP on their Taxable Income can be carried forward to offset against future Taxable Income, except for income from intellectual property. ii)Losses related to Qualifying Income cannot be used to offset Taxable Income, transferred, or carried forward. Further, QFZPs cannot transfer or receive Tax Losses from other Taxable Persons. |
| Outsourcing of core income generating activity: | In case a Free Zone Person outsources a core income-generating activity to another entity within a Free Zone or Designated Zone, adequate supervision over the activity by the Free Zone Person is important where it should be capable of overseeing and controlling the activity adequately, and ensuring that the resources of the entity performing the activity are sufficient for the specific services rendered to the Free Zone Person, without any duplication of assets, employees, or expenses across multiple Free Zone Persons. For distribution activity, core income generating activity must be outsourced within a designated zone. |
| Treatment of Mixed use property: | In the case of a hotel building in a Free Zone, revenue allocation between commercial and non-commercial units should be determined. This allocation can be based on the records of the land registry department or alternative methods like rental or property value. The aim is to achieve a fair and reasonable arm’s length allocation considering the specifics of each case. Generally, retail outlets and restaurants are classified as commercial units, while rooms, conference rooms, and banquet halls are considered non-commercial units. |
| Ancillary activities: | Qualifying Activities include ancillary activities, which are those necessary for the performance of the main activity or contributing minorly to the main Qualifying Activity and are closely related to it. If an ancillary activity is conducted independently of the main Qualifying Activity, it will not be considered a Qualifying Activity. Determining whether an activity is ancillary depends on the specifics of the main Qualifying Activity conducted by the Free Zone Person and will be assessed based on the particular facts and circumstances of the case. |
| Income from Qualifying Intellectual Property: | i) In order to benefit from the 0% rate on Qualifying income from Qualifying Intellectual property, a QFZP must be able to demonstrate a nexus between Qualifying expenditure and income from Qualifying Intellectual Property. In such cases, a QFZP must set up an appropriate tracking system in order to avail the benefit. ii) While calculating the Qualifying income from Intellectual Property, the sum of Qualifying expenditure and Uplift expenditure shall be lower of the following- – 130% of Qualifying Expenditure – Overall Expenditures |
| Compliances: | 1. A QFZP is not required to prepare separate Financial Statements for its Qualifying Income and its other income and should have sufficient documentation to demonstrate the calculation of Qualifying Income. 2. A QFZP is not required to prepare separate Financial Statements for any of its branches. |
Here are the main highlights from this CT guide regarding Qualifying activities –
| 1. Manufacturing of goods or materials: | 1. Activities that might be considered ancillary to the Qualifying Activity of manufacturing goods or materials, provided they naturally and integrally complement the main Qualifying Activity and meet the conditions for ancillary activities, include post-sale activities and customer support. Also, manufacturing does not include repairs. 2. Intangible items like software, which can be sold independently of a physical asset, are not considered goods under the definition for this Qualifying Activity. Therefore, the creation of software, ERPs, automation tools, and similar items will not be classified as the manufacturing of goods or materials. However, Software embedded in hardware (i.e. it is inherently part of the hardware) generally would be considered as goods. 3. Goods that are manufactured in the UAE do not need to pass through a Designated Zone, however, the distribution activity is required to be conducted in or from a Designated Zone in order to be a Qualifying Activity. However, the question remains unresolved as to whether a manufacturer producing goods or materials within a free zone, which isn’t designated as such, would have their distribution activities from that free zone considered as Qualifying activities. |
| 2.Trading of Qualifying Commodities: | 1. Qualifying Commodities encompass metals, minerals, energy, and agricultural products traded in their raw form on a Recognized Commodities Exchange Market. Recognized Commodities Exchange Market means the following- – Markets that are established in the UAE and licensed and regulated by the relevant authorities (such as Central Bank of the UAE, the Dubai Financial Services Authority of the Dubai International Financial Centre (DFSA), the Financial Services Regulatory Authority of the Abu Dhabi Global Market (FSRA), or the Securities and Commodities Authority (SCA). For example, the Dubai Gold & Commodities Exchange in the UAE) or – Markets are of equal standing if established outside the UAE(such as the Chicago Board of Trade, and the London Metal Exchange). 2. The Qualifying Commodity needs to be in a form that is traded on a Recognised Commodities Exchange Market. Metals, minerals, energy, and agriculture commodities that are traded on a Recognised Commodities Exchange Market will be deemed to be in raw form when they meet the conditions to be traded on the said exchange (for example, gold being 99.4% purity in bullion form). The trade itself does not need to be performed through an exchange. 3. Raw form refers to commodities in their natural, unprocessed state, with no added value, traded on recognized commodities exchange markets before any processing or transformation. 4. Under agricultural commodities it includes products like wheat, corn, and soybeans. 5. Under Energy commodities it includes crude oil and natural gas. 6. Under Metals it includes items like gold, silver bars, and aluminum ingots. |
| 3. Holding of shares and other securities for investment purposes: | 1. The active trading of shares and other securities would not constitute a Qualifying Activity. 2. If the intention to hold can be demonstrated for an uninterrupted period of at least 12 months, Shares and other securities shall be deemed to be held for investment purposes and accordingly benefit shall be available. 3. Income derived from securities backed by receivables from non-financial asset is excluded from the Qualifying Activity. However, securities backed by receivables from a financial asset will be considered under Qualifying Activity. |
| 4. Ownership, management and operation of ships: | 1. Ships used for local transportation or leisure or recreational purposes, or as floating hotels, restaurants or casinos is not considered under Qualifying Activity. 2. Business consisting solely of maintenance, fit-out or repairing Ships will not be considered as a Qualifying Activity. 3. It also does not include the leasing of shipping containers, unless that activity is ancillary to a shipping business. |
| 5.Fund management services and Wealth and investment management services: | 1. Fund management services and Wealth and investment management services will be considered as Qualifying Activities if they are subject to the regulatory oversight of the relevant Competent Authority in the UAE. The following shall be considered as Competent Authority in the UAE:- – Central Bank of the United Arab Emirates – The Dubai Financial Services Authority – The Financial Services Regulatory Authority of the Abu – – Dhabi Global Market or – The Securities and Commodities Authority 2. Single Family Office and Multi Family Office would not be considered under Qualifying Activity of wealth and investment management services if it is not appropriately regulated by a relevant Competent Authority. |
| 6.Treasury and financing services to Related Parties: | 1. Under this activity, the definition of Related Parties includes Domestic Permanent Establishments and self-investment. Income from investment of surplus funds such as Interest from bank deposits, will be treated under Qualifying Activity as it will be considered as Treasury and Financing services to oneself. 2. The activity of Treasury and Financing is widely defined and includes cash pooling, cash management, risk management, investment management and financing. |
| 7.Financing and leasing of Aircraft: | Sub-leasing of Aircraft will fall within the scope of Qualifying activity. |
| 8.Distribution of goods or material in or from a Designated Zone | 1. A key feature of distribution activity is that the distributor holds the title to the products which differentiates it from Logistics services. 2. As per MD 265 of 2023, definition of “Distribution of goods or material in or from a Designated Zone” includes buying and selling of goods, materials, component parts or any other items that are tangible or movable. Accordingly, distribution of intangible products and services such as licenses, software and financial products/ services will not be covered under distribution activity. However, the guide has further clarified that if the product is embedded onto a hardware, income for which is not separately identifiable, they can still qualify for Distribution activity. 3. The concept of ‘end-user’ is now defined in the Guide. End-user is the person who eventually uses the product for its intended purpose, whether they may be personal, commercial or industrial. Accordingly, if a distributor is engaged in selling goods to a customer who is end-user (i.e., uses or consumes the product), then such activity will not be considered as a Qualifying activity. A QFZP has to conduct necessary due-diligence (obtain KYC, undertaking etc. from the customer) to demonstrate that the customer is not an end-user in order to fall within the scope of the Distribution as a Qualifying activity. 4. Under Ministerial Decision No. 265 of 2023 on Free Zone, it was not clear whether High Seas Sales (Third port shipment) is covered under Qualifying activity -Distribution of goods or materials in or from a Designated Zones, as goods do not physically enter UAE. Now the new guide has clarified that High Seas Sales (Third Port Shipment) if undertaken from Designated Zones shall be covered under Qualifying Activities. 5. There are no limitations on the mode of distribution. For goods that are procured from UAE itself and sold in UAE/outside, they do not need to pass through a Designated Zone. The requirement of distributed goods to enter a Designated Zone only applies in case goods are imported into the UAE and then sold. |
| 9. Logistics services: | 1. Logistics services do not include the movement of people. 2. Last-mile delivery services outside of the Free Zone in the UAE or in a foreign country will also be considered as a Qualifying Activity provided QFZP performs most of its logistics services within a Free Zone for its customers in the UAE outside a Free Zone or foreign customers. |